GitLab Geo configuration
Note: This is the documentation for installations from source. For installations using the Omnibus GitLab packages, follow the Omnibus GitLab Geo nodes configuration guide.
- Install GitLab Enterprise Edition on the server that will serve as the secondary Geo node. Do not login or set up anything else in the secondary node for the moment.
-
Setup the database replication (
primary (read-write) <-> secondary (read-only)topology). - Configure GitLab to set the primary and secondary nodes.
- Follow the after setup steps.
This is the final step you need to follow in order to setup a Geo node.
You are encouraged to first read through all the steps before executing them in your testing/production environment.
Setting up GitLab
Notes:
- Do not setup any custom authentication in the secondary nodes, this will be handled by the primary node.
- Do not add anything in the secondaries Geo nodes admin area (Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes). This is handled solely by the primary node.
After having installed GitLab Enterprise Edition in the instance that will serve as a Geo node and set up the database replication, the next steps can be summed up to:
- Configure the primary node
- Replicate some required configurations between the primary and the secondaries
- Configure a second, tracking database on each secondary
- Configure every secondary node in the primary's Admin screen
- Start GitLab on the secondary node's machine
Prerequisites
This is the last step of configuring a Geo node. Make sure you have followed the first two steps of the Setup instructions:
- You have already installed on the secondary server the same version of GitLab Enterprise Edition that is present on the primary server.
- You have set up the database replication.
- Your secondary node is allowed to communicate via HTTP/HTTPS and SSH with your primary node (make sure your firewall is not blocking that).
- Your nodes must have an NTP service running to synchronize the clocks. You can use different timezones, but the hour relative to UTC can't be more than 60 seconds off from each node.
- You have set up another PostgreSQL database that can store writes for the secondary. Note that this MUST be on another instance, since the primary replicated database is read-only.
Some of the following steps require to configure the primary and secondary nodes almost at the same time. For your convenience make sure you have SSH logins opened on all nodes as we will be moving back and forth.
Step 1. Adding the primary GitLab node
-
SSH into the primary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Add this node as the Geo primary by running:
bundle exec rake geo:set_primary_node
Step 2. Updating the known_hosts file of the secondary nodes
-
SSH into the secondary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
The secondary nodes need to know the SSH fingerprint of the primary node that will be used for the Git clone/fetch operations. In order to add it to the
known_hostsfile, run the following command and typeyeswhen asked:sudo -u git -H ssh git@<primary-node-url>Replace
<primary-node-url>with the FQDN of the primary node. -
Verify that the fingerprint was added by checking
known_hosts:cat /home/git/.ssh/known_hosts
Step 3. Copying the database encryption key
GitLab stores a unique encryption key in disk that we use to safely store
sensitive data in the database. Any secondary node must have the
exact same value for db_key_base as defined in the primary one.
-
SSH into the primary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Execute the command below to display the current encryption key and copy it:
bundle exec rake geo:db:show_encryption_key -
SSH into the secondary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Open the secrets file and paste the value of
db_key_baseyou copied in the previous step:editor /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json Save and close the file.
Step 4. Regenerating the authorized keys in the secondary node
IMPORTANT: Since GitLab 10.0
~/.ssh/authorized_keysno longer can be used, and this step is deprecated. Instead, follow the instructions on configuring SSH authorization via database lookups (for both primary AND secondary nodes).
Regenerate the keys for ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
(HTTPS clone will still work without this extra step).
-
On the secondary node where the database is already replicated, run:
# Installations from source sudo -u git -H bundle exec rake gitlab:shell:setup RAILS_ENV=production
This will enable git operations to authorize against your existing users.
New users and SSH keys updated after this step, will be replicated automatically.
Step 5. Enabling hashed storage (from GitLab 10.0)
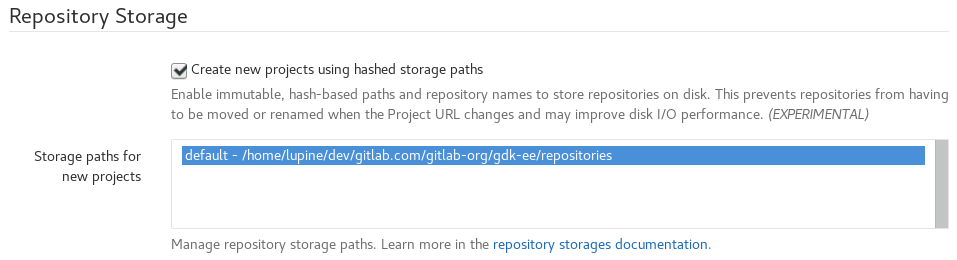
- Visit the primary node's Admin Area ➔ Settings
(
/admin/application_settings) in your browser -
In the
Repository Storagessection, checkCreate new projects using hashed storage paths:
Using hashed storage significantly improves Geo replication - project and group renames no longer require synchronization between nodes - so we recommend it is used for all GitLab Geo installations.
Step 6. Enabling the secondary GitLab node
-
SSH into the secondary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Create a new SSH key pair for the secondary node. Choose the default location and leave the password blank by hitting 'Enter' three times:
sudo -u git -H ssh-keygen -b 4096 -C 'Secondary GitLab Geo node'Read more in additional info for SSH key pairs.
-
Get the contents of
id_rsa.pubthe was just created:sudo -u git cat /home/git/.ssh/id_rsa.pub Visit the primary node's Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes (
/admin/geo_nodes) in your browser.Add the secondary node by providing its full URL and the public SSH key you created previously. Do NOT check the box 'This is a primary node'.
Added in GitLab 9.5: Choose which namespaces should be replicated by the secondary node. Leave blank to replicate all. Read more in selective replication.
Click the Add node button.
After the Add Node button is pressed, the primary node will start to notify changes to the secondary. Make sure the secondary instance is running and accessible.
The two most obvious issues that replication can have here are:
- Database replication not working well
- Instance to instance notification not working. In that case, it can be
something of the following:
- You are using a custom certificate or custom CA (see the Troubleshooting section)
- Instance is firewalled (check your firewall rules)
Step 7. Replicating the repositories data
Getting a new secondary Geo node up and running, will also require the repositories data to be synced.
With GitLab 9.0 the syncing process starts automatically from the secondary node after the Add Node button is pressed.
Currently, this is what is synced:
- Git repositories
- Wikis
- LFS objects
- Issue, merge request, and comment attachments
- User, group, and project avatars
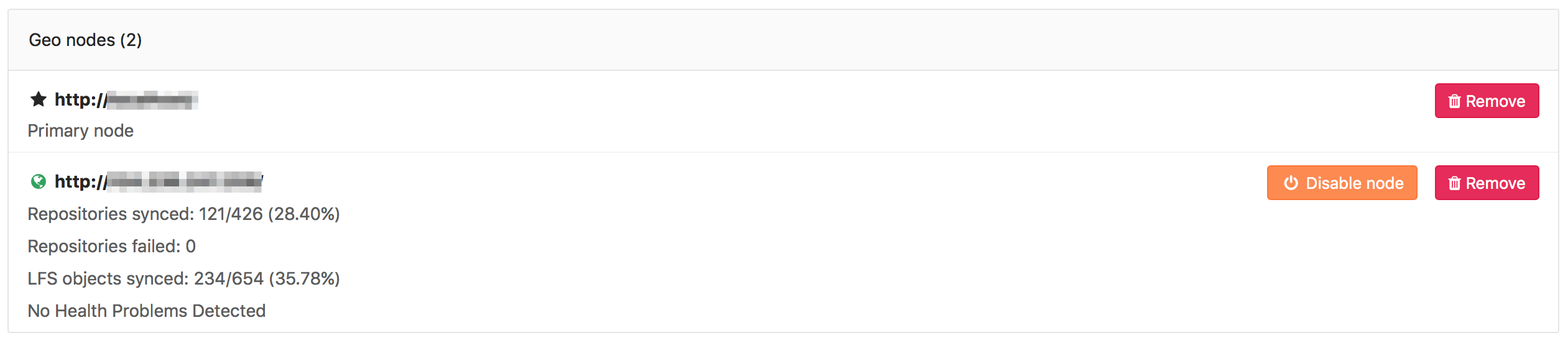
You can monitor the status of the syncing process on a secondary node
by visiting the primary node's Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes (/admin/geo_nodes)
in your browser.
Please note that if git_data_dirs is customized on the primary for multiple
repository shards you must duplicate the same configuration on the secondary.
Disabling a secondary node stops the syncing process.
With GitLab 8.14 this process is started manually from the primary node.
You can start the syncing process by clicking the "Backfill all repositories"
button on Admin > Geo Nodes screen.
On previous versions, you can use rsync for that:
Make sure rsync is installed in both primary and secondary servers and root
SSH access with a password is enabled. Otherwise, you can set up an SSH key-based
connection between the servers.
-
SSH into the secondary node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Assuming
1.2.3.4is the IP of the primary node, run the following command to start the sync:# Installations from source rsync -guavrP root@1.2.3.4:/home/git/repositories/ /home/git/repositories/ chmod ug+rwX,o-rwx /home/git/repositories
If this step is not followed, the secondary node will eventually clone and fetch every missing repository as they are updated with new commits on the primary node, so syncing the repositories beforehand will buy you some time.
While active repositories will be eventually replicated, if you don't rsync, the files, any archived/inactive repositories will not get in the secondary node as Geo doesn't run any routine task to look for missing repositories.
Next steps
Your nodes should now be ready to use. You can login to the secondary node
with the same credentials as used in the primary. Visit the secondary node's
Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes (/admin/geo_nodes) in your browser to check if it's
correctly identified as a secondary Geo node and if Geo is enabled.
If your installation isn't working properly, check the troubleshooting section.
Point your users to the after setup steps.
Selective replication
Read Selective replication.
Adding another secondary Geo node
To add another Geo node in an already Geo configured infrastructure, just follow the steps starting from step 2. Just omit the first step that sets up the primary node.
Additional information for the SSH key pairs
Read Additional information for the SSH key pairs.
Troubleshooting
Read the troubleshooting document.